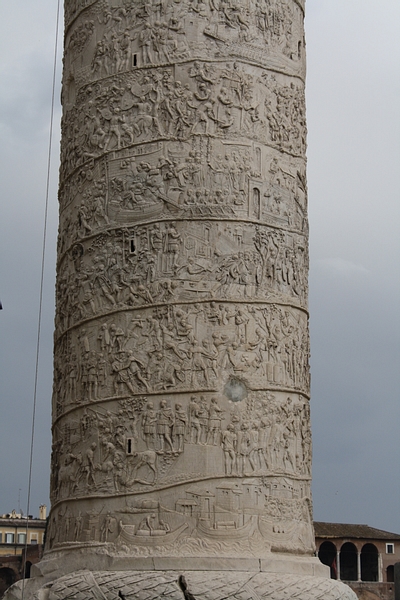
Decebalus (c. 87-106 CE) was the king of Dacia (roughly modern-day Romania and Moldova) who fought two wars with Rome under Trajan (in 101-102 CE and 105-106 CE) in defense of his kingdom.
Trajan (r. 98-117 CE) was renewing a conflict between Rome and Dacia which was thought to have ended when Domitian (r. 81-96 CE) brokered an earlier peace agreeing to pay Dacia a certain amount each year with no stipulation for a conclusion. Trajan objected to this treaty while Decebalus felt it was only fair since, to his mind, Rome had initiated the earlier war. He defended Dacia ably against Trajan's assault and is honored as the last and greatest king of Dacia.
When the second war with Rome went against him, Decebalus continued to evade Trajan's troops by moving to different fortresses in the mountains. He was finally tracked down, however, and committed suicide rather than be taken to Rome as a feature in a Roman triumph. He is remembered as a just and able monarch who defended the country against Roman aggression and died in the cause of freedom.
Rise to Power
The people of Dacia were originally a confederacy of tribes who united under a single chief. The first king, Rubobostes, defeated the Celts in the region and established a semblance of national unity. The second king, Oroles, continued this initiative and united the different tribes under his leadership, consolidating the regions into a tighter confederacy. It would be the third king, Burebistas (c. 80-44 CE), who is the best historically attested of these monarchs, who succeeded in establishing Dacia as a nation. He conquered the remaining hostile tribes, enlarged Dacian territory, reformed the military, and instituted laws.
Burebistas supported Pompey in his civil war with Julius Caesar in 49-48 BCE, and the fact that his support mattered attests to his power and Dacia's prestige at this time. Caesar was so offended by Burebistas' support of his rival, in fact, that he considered invading Dacia in retaliation but was assassinated in 44 BCE; the same year Burebistas was also killed. The Dacian aristocracy opposed Burebistas' concept of a strong central government as they felt it reduced their individual power. He was assassinated probably only a few months after Caesar, and Dacia split into four separate principalities. By the time of Augustus Caesar (r. 27 BCE-14 CE), the country had further divided into five territories with the strongest ruled by a king named Cotiso who was betrothed to Augustus' daughter.
Cotiso was overthrown by his own people and, seemingly, at the instigation of Rome; exactly why this happened is unclear. Another king named Douras rose in his place who may have initially been supported by Rome but, if so, he quickly turned against them. He won the support of the people by launching raids into the Roman territory of Moesia for plunder and, as support for him grew, claimed all of Dacia subject to his rule. It is at this point that Decebalus enters history as a general in Douras' army.
Nothing is known of Decebalus' early life or ancestry, although many theories have been suggested. His name may have been Diurpaneus or Dorpaneus (though this is contested) and “Decebalus” is a title meaning “brave of heart” or “stronger than the hearts of ten men” which he became known by following his victory over Domitian's army. Scholar Philip Matyszak claims that the title “translates roughly as 'Brave Heart' and suggests that Decebalus liked to lead from the front” (216). This interpretation is probably correct as it is clear that Decebalus was popular with his men and, by 87 CE, Douras was forced to abdicate and Decebalus became king of a united Dacia.
First War with Rome
Douras and Decebalus raided Roman Moesia in 85 CE, killing the governor Gaius Oppius Sabinus. Domitian, emperor of Rome at this time, mobilized his army to strike at Dacia in 86 CE in order to stop the constant raids, which Decebalus had continued, and also as a punitive measure to avenge Sabinus. Decebalus responded with an offering to negotiate a peace, but Domitian refused and sent the general Cornelius Fuscus (died 86 CE) at the head of a large army to destroy the Dacians.
The Roman historian Cassius Dio, who is the main source of Rome's wars with Dacia (along with the engravings of the campaign on Trajan's Column), notes how Decebalus laughed at this threat and sent word back that “his terms for peace were that every Roman should pay him an annual tribute of two obols. Failure to pay up would provoke war and unleash a torrent of misfortunes upon the Romans” (Epitome 68.6). Domitian was enraged and ordered Fuscus into battle.
Matyszak, following the narrative of Cassius Dio, writes:
Decebalus' cavalier attitude was inspired by his mastery of his own terrain of steep hills, thick woods, and rapid rivers. Furthermore, at some point between the reign of Burebistas and Decebalus, the Dacians had built a redoubt in the Orastie Mountains. This was a complex series of fortresses, watchtowers, and walls spread out over some 193 square miles (500 square kilometers). Modern archaeological research on these structures confirms that the Dacians were excellent architects and engineers, and their forts must have seemed secure against the worst the Romans could do. (217)
Fuscus was killed in battle following an ambush and the legion suffered heavy casualties. They retreated back to Roman Moesia having lost a significant number of their troops, weapons, and even the legion's eagle standard. Domitian was far from interested in suing for peace, however, and sent another legion into Dacia through the pass known as the Iron Gates at Tapae, where they met the Dacian forces and defeated them.
As each party had now won a clear victory, and both had other matters to attend to, negotiations were opened. Decebalus swore to respect the boundaries with Rome and refrain from hostilities and Domitian agreed to send him a workforce to help repair the damage done to his kingdom as well as engineers and an annual payment. Domitian died soon after this and was succeeded by Nerva (96-98 CE) who concentrated on strengthening Rome itself and ignored the Dacian situation. After two years, he abdicated in favor of Trajan, his adopted son, and Trajan made Dacia one of his priorities.
The Trajan Wars
Trajan considered it an insult that Rome, who had been wronged by Dacia through the raids and insolence of its kings, should have to pay a yearly subsidy which would only go toward making Dacia even stronger and more insolent. Cassius Dio observes how Trajan “also observed that their power and their pride were increasing” and understood he needed to deal with Dacia before it became a more serious problem (History, 68.6).
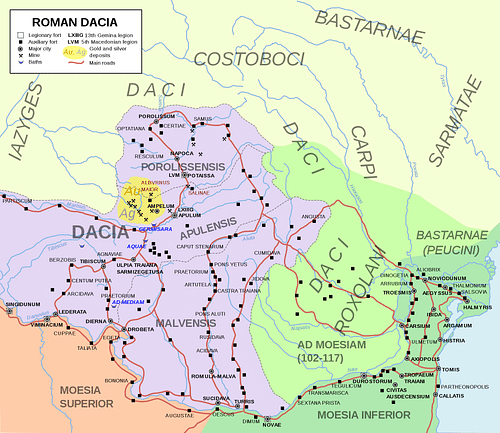
Trajan marched on Dacia in 101 CE and systematically reduced the fortresses along the line by making use of auxiliary troops who knew the area and could easily scale the hills and navigate the rivers and streams. Further, in an effort to protect his soldiers against the Dacian hand weapon known as the falx (a kind of scythe), he improved and modified their helmets and armor. His campaign was a seamless success which captured the Dacian capital of Sarmizegetusa as well as Decebalus' sister.
Decebalus sued for peace and negotiations were opened. According to Cassius Dio:
Decebalus was in a position where he was prepared to agree without exception to every demand which the Romans made – not that he intended to keep to any agreement, but so that he could gain time to recover from his present setbacks. (History, 68.9)
He agreed to surrender all his weapons, end the annual payments from Rome, return Roman deserters who were in his army, relinquish all gains in territory he had taken from Rome, pull down his fortifications, and ally himself to the Roman cause as a client king. Henceforth, he said, friends and enemies of Rome would also be his and he would never lift a hand against the Roman state again.
Trajan accepted his peace terms and withdrew from Dacia, returning to Rome, but left a garrison of soldiers behind in Sarmizegetusa to ensure Decebalus' compliance with the treaty. In Rome, Trajan celebrated his triumph and turned his attention to other matters while, in Dacia, Decebalus began rebuilding and restoring his fortifications and sending out invitations throughout the region to join his army in destroying Rome.
The garrison in Sarmizegetusa informed Trajan that Decebalus had broken the peace and he again marched on Dacia in 105 CE. Decebalus sent assassins to kill him on the march since he knew that Trajan was in the habit of visiting with his men without a bodyguard and should be easily taken, but one of these assassins was arrested for acting suspiciously and, under torture, revealed the plot. Trajan continued his march while Decebalus tried another tactic: he sent word to Trajan's general Longinus that he wanted peace and invited Longinus to come and work out the details. When Longinus arrived, however, he was arrested and Decebalus sent word to Trajan that he would return Longinus only if Trajan withdrew.
Longinus, however, was not about to be used in this way and persuaded a freedman (a former slave, now a servant) in the fortress to bring him poison. He then told Decebalus he wanted this man sent to Trajan with a message regarding negotiations and how to set him free. Once the man was sent, Longinus killed himself with the poison. Decebalus then sent another messenger to Trajan demanding that he return the freedman who had helped Longinus in return for Longinus' body and ten other captives still living. Trajan not only refused but kept the messenger Decebalus had sent with the offer.
Trajan renewed his march on Dacia but, this time, in order to send a clear message that he was not to be trifled with, he stopped at the banks of the Danube and built an enormous bridge. Cassius Dio comments on this, writing:
Trajan constructed over the Ister [Danube] a stone bridge for which I cannot sufficiently admire him. Brilliant, indeed, as are his other achievements, yet this surpasses them. For it has twenty piers of squared stone one hundred and fifty feet in height above the foundations and sixty in width, and these, standing at a distance of one hundred and seventy feet from one another, are connected by arches. How, then, could one fail to be astonished at the expenditure made upon them, or at the way in which each of them was placed in a river so deep, in water so full of eddies, and on a bottom so muddy? For it was impossible, of course, to divert the stream anywhere. (Epitome, 68.13)
This bridge, of course, took time to build and meanwhile Decebalus attacked the garrisons Trajan had left in Dacia earlier and redoubled his efforts at rebuilding his forts and defenses. Decebalus reached out to friends and former enemies to join him in resisting the Roman invasion since, as he said, they would do better to ally with him now than wait for Rome to subdue them separately later. Even so, he recognized from his past defeat that open battle with the Romans under Trajan would be a tragic mistake and so, as Trajan marched over his new bridge and into Dacia, Decebalus launched a guerrilla war.
The Roman army marched in two columns straight for the capital of Sarmizegetusa, placed it under siege, and took it. Decebalus fled to the higher ground of his fortresses in Transylvania. Trajan wanted Decebalus found and brought to him and, finding him gone, had the city razed to the ground. Using the same kinds of troops he had on his first Dacian campaign, Trajan sent his men into the mountains to hunt Decebalus down.
Recognizing that he could not outrun the Romans forever, Decebalus gathered his remaining chieftains for a great feast and then killed himself by slashing his own throat. A Roman cavalryman named Maximus had only just located the fort where the banquet was being held and ran into the room just as Decebalus committed suicide. Maximus cut off his head and brought it to Trajan. Trajan then ordered a mass round up of Dacians loyal to Decebalus to be brought as prisoners to Rome and directed that their lands, and those of many others, were forfeit to Roman citizens. Matyszak writes:
The native peoples were either extirpated or driven from their lands and settlers were brought in from all over the Empire to take their place. One consequence of this is that of all modern languages, Romanian is among the closest to Latin, and the modern name of the country reflects the extent to which Trajan's settlers made themselves at home. (224)
Prior to his flight from the capital, Decebalus had ordered his treasure and his rich wardrobe hidden in caves and nooks and even at the bottom of the river so they would not fall into Roman hands. After his death, though, these locations were betrayed to the Romans by one of his men who had been taken prisoner, and the treasures were taken away as plunder along with the people of Dacia.
Conclusion
Decebalus' name fell into obscurity until the 19th century CE when Romania, like many other European nations, was searching for a national hero in the wake of their independence. Decebalus was the obvious choice and, throughout the 20th century CE and into the present, he has been honored on bank notes, in literature, and in sculpture. The most famous of these is the Decebalus Rex monument, commissioned by a Romanian businessman and carved into a cliff at the Iron Gates in Romania between 1994-2004 CE, an image of the great king's face looking down over the Danube and an ancient plaque, on the far side of the river, Trajan had placed to commemorate the road he built in his conquest of Dacia.
Although he is best known to history for his wars with Rome, Decebalus was an able administrator who enlarged and improved upon his kingdom. He may also have continued the religious reforms which were begun under Burebistas. The religion of Dacia centered on the deity Zalmoxis (known as Zalmoxism) who was a sky god and possibly lead-deity of a pantheon about whom little is now known. Zalmoxis promised his adherents eternal life, especially those who died bravely in battle, and it is thought that Decebalus emphasized this aspect of the faith to encourage his troops.
Death was not the end of life for those who believed in Zalmoxis but was only a change of place; the dead moved to the afterlife as easily as someone would walk from one region of Dacia to another. This belief, which was shared by the tribes within and outside the kingdom of Dacia, would have strengthened their resolve in resisting the Romans.
Whatever part religion played in the warrior ethos of Dacia, it required a strong leader to impart that kind of inspiration to his troops. Decebalus was precisely that kind of king who was able to command loyalty from his supporters and respect from his enemies. Cassius Dio praises him as “a master of both the theory and the practice of warfare” and notes how “he knew well not only how to follow up a victory but also how to handle a defeat” (Epitome, 67.6). Even on Trajan's Column, which gives the story of the Dacian Wars in images, Decebalus is depicted as an admirable adversary.
Modern-day Romania lists Burebistas, Decebalus, and Trajan as the founding fathers of the country: Burebistas for establishing the country, Decebalus for defending it, and Trajan for populating it with Roman citizens, who would significantly influence the development of culture and language, after the second war was won by Rome. Of these three, however, Decebalus is held in special regard for his efforts to preserve Dacia as a free and independent nation.