Antigonus I Monophthalmus ("the One-Eyed") (382 -301 BCE) was one of the successor kings to Alexander the Great, controlling Macedonia and Greece.
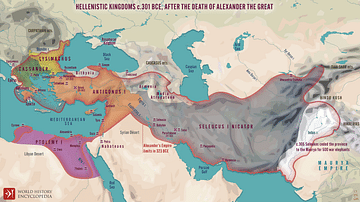
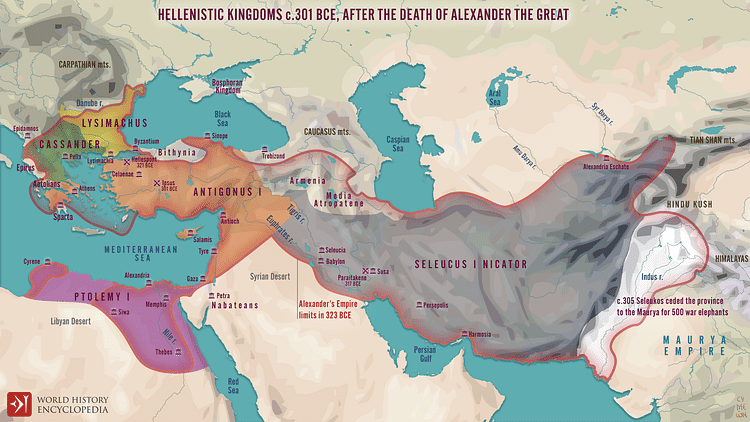
When Alexander the Great died in 323 BCE, a conflict known as the Wars of the Diadochi ensued over his massive empire stretching from Greece to India. It was eventually divided among three of his most loyal generals and their families - Ptolemy I and his descendants, the Ptolemaic Dynasty (among them Cleopatra VII) would rule Egypt; Seleucus I Nicator and his family ruled Syria and the Near Eastern provinces, and lastly, the descendants of Antigonus ruled Macedonia and Greece. Although this was the way it ended, it was not how it began.
Alexander's General
Antigonus was a Macedonian general and nobleman who served ably under both Alexander the Great and his father Phillip II (r. 359 BCE - 336 BCE). After Phillip's death by assassination at the hands of his former bodyguard Pausanias, Alexander decided to follow his father's dream and cross the Hellespont into Anatolia to meet and defeat Darius III (r. 336-330 BCE) and conquer the Achaemenid Empire. Antigonus, at the age of 60, followed Alexander on this campaign.
After crossing the Hellespont, Alexander marched his troops northward, pausing briefly to give homage to the heroes of Homeros, Achilles and the Greeks fallen in the Troyan War. He then moved southward defeating the Persians at the Battle of Granicus in May 334 BCE. Before leaving to eventually meet and defeat Darius III at the Battle of Issus (November 333 BCE), Alexander left Antigonus as satrap of Phrygia (western Anatolia) with a force of 1500 troops to help defend the satrapy, maintaining a capital at Celanae. He would remain there for the remainder of Alexander's war against the Persians. Antigonus' primary responsibility was to maintain Alexander's lines of supply and communication; however, his stay there did not go smoothly. After Alexander and his massive army moved further south into Syria, the Persians attempted to regain some of the territory they had lost. Antigonus and his army had to defend his domain in Phrygia on three different occasions, winning all three battles. One of these battles was against the Greek mercenary Memnon (loyal to Darius) who had recently been defeated at Granicus.
In 323 BCE Alexander died in Babylon, but just prior to dying, Alexander handed his signet ring to his senior cavalry officer Perdiccas, a possible indication to some that Alexander was naming him as a successor. Perdiccas immediately brought the other generals together to discuss the future of the empire. Meleager, an infantry leader, was considered (at least in his own mind) to be second in command - a position he would not remain in for long. Perdiccas had him executed: an indication that a fight over the empire lay ahead. The major question remained: who was to rule? Perdiccas elected to wait until Roxanne and Alexander's child was born, the son who would become Alexander IV. However, the young Alexander would never rule, as both Roxanne and young Alexander were executed by Antipater's son Cassander in 310 BCE, solving the entire inheritance problem.

The generals finally agreed to divide Alexander's empire in the Partition of Babylon. The partition granted Antigonus the satrapy of Phrygia as well as Pamphylia and Lycia (northwestern Anatolia). Antipater remained as regent of Macedonia while his son, Cassander, received Caria (southwestern Anatolia). Ptolemy remained as regent in Egypt. Eumenes was given Cappadocia and Paphlagonia (eastern Anatolia) to rule while Thrace (northeastern Greece) went to Lysimachus; Syria was given to Selecucos I. This division, however, was not to remain. There would be 20 more years of war. Alliances came and went, peace was inconsistent and jealousy remained throughout.
Wars of the Diadochi
The arguments over territory began when Perdiccas became angry at Antigonus because he refused to help Eumenes keep control of his allotted territory. Antigonus wanted to avoid conflict with Periccas so he and his 13-year-old son Demetrius sought refuge in Macedonia, gaining favor of Antipater - they united against Perdiccas and Eumenes. Eumenes was defeated and imprisoned in 321 BCE. Next, Antigonus allied himself with Antipater, Ptolemy, and Lysimachus against Perdiccas. Perdiccas died by assassination in 321 BCE thus ending the alliance.
Upon the death of his father Antipater in 319 BCE, Cassander was denied the regency of Macedonia; Antipater had believed him too young to oppose the other regents. Instead, he named Polyperchon as the new regent, who allied himself with Eumenes to maintain his regency (even though Eumenes was still imprisoned at the fortress at Nora). The other regents refused to recognize Polyperchon's authority, fearing a threat to their own regency. Eumenes escaped from his imprisonment, however, to aid Polyperchon. Antigonus fought Eumenes twice, defeating him both times, with the result that Eumenes' famed Silver Shields, an elite Macedonian regiment, turned him over to Antigonus who summarily had him executed.
In order to gain the regency he felt he deserved, Cassander turned to Antigonus and Lysimachus for help. Antigonus wanted control of Macedonia, so he agreed to the alliance. Cassander gained control of Macedonia forcing Polypheron out. With Eumenes defeated, Antigonus controlled much of the eastern Mediterranean. He and his forces marched into Babylon causing Seleucus to flee to Egypt and form an alliance with Ptolemy. After Antigonus besieged the island city of Tyre, he moved his forces into Syria; however, his advances were stopped by Ptolemy and Seleucus.
This desire to reunite Alexander's kingdom under his leadership brought Antigonus against the combined forces of Ptolemy, Lysimachus, Cassander, and Seleucus. After Antigonos's son Demetrius was defeated by Ptolemy at the Battle of Gaza, Seleucus took back Babylon. With this defeat, a limited peace was declared, lasting from 315 to 311 BCE. The peace agreement left Antigonus in control of all of Asia Minor and Syria. The uneasy peace ended when Antigonus decided to make another move at claiming Macedonia and Greece by extending a peace offering to the Greek city-states granting them self-government and withdrawal of all Macedonian troops.
The historian Diodorus spoke of this extension of a helping hand when he stated in his World History:
All the Greeks should be free, exempt from garrisons, and autonomous. The soldiers carried the motion and Antigonus dispatched messengers in every direction to announce the resolution. He calculated as follows: The Greeks' hopes for freedom would make them willing allies in the war, while the generals and satraps in the eastern satrapies, who suspected Antigonus of seeking to overthrow the kings who had succeeded Alexander, would change their minds and willingly submit to his orders when they saw him clearly taking up the war on their behalf.
While he gained the support of the Greek city-states, Antigonus incurred the wrath of the others who allied against him: Lysimachus invaded Asia Minor from Thrace, securing the old Greek Ionian cities and Seleucus marched through Mesopotamia and Cappadocia. The wars returned and continued for a number of years.

Ptolemy, Seleucus, Cassander, and Lysimachus finally combined their forces and met Antigonus in Phrygia in 301 BCE. At the age of 80, Antigonus died in the Battle of Ipsus from the simple throw of a javelin. Demetrius fled back to Macedonia to hopefully secure his rule there. For almost two more decades, he and his son Antigonus Gonata fought for Macedonia, eventually gaining control, establishing the Antigonid dynasty.
Conclusion
How can one assess Antigonus? Was he a great general? Plutarch in his Life of Demetrios said:
If Antigonus could only have borne to make some trifling concessions, and if he had shown any moderation in his passion for empire, he might have maintained for himself till his death and left to his son behind him the first place among the kings. But he was of a violent and haughty spirit; and the insulting words as well as actions in which he allowed himself could not be borne by young and powerful princes, and provoked them into combining against him.
Plutarch later stated that as the armies of his enemies came toward him at the Battle of Ipsus, he was confident that Demetrius would still rescue him, but Demetrius was engaged elsewhere in the battle. Antigonus remained that way "until he was borne down by a whole multitude of darts, and fell."